الألياف البصرية مقابل الاتصالات الساتلية
الاتصالات الألياف البصرية والاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية هي التقنيات الرائدة التي هي ثورة في عالم الاتصالات. كلا التقنيتين لديها مزايا والقيود التي تجعلها مناسبة لنوع معين من التطبيقات. هذه المادة سوف توفر لمحة عامة عن تقنيات الألياف والاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية البصرية وتقديم مقارنة بين ميزات والقضايا ذات الصلة.
الاتصالات الألياف البصرية
الألياف الضوئية الاتصالات ينقل المعلومات عن طريق إرسال نبضات من الضوء (باستخدام الليزر) من خلال الألياف البصرية. فقدان إشارة منخفضة في الألياف البصرية ومعدل البيانات عالية أنظمة الإرسال، تسمح إشارات مع ارتفاع معدلات البيانات (تتجاوز عدة جيجابايت في الثانية) للسفر لمسافات طويلة (أكثر من 100 كم) دون الحاجة لإعادة الإرسال أو مكبر للصوت. وعلاوة على ذلك، وذلك باستخدام الطول الموجي بالتقسيم (WDM) يسمح للألياف واحد لتحمل إشارات متعددة (حتى 10 إشارات مختلفة) الإرسال المتعدد جيجابايت في الثانية. يقدم الألياف الضوئية الاتصالات عرض النطاق الترددي العالي جدا، مناعة ضد التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي، والتأخير غير موجودة والحصانة من اعتراض عن طريق الخارجية. في 1980s و 1990s، كانت هناك صلة بين القارات معا باستخدام الألياف البصرية تحت البحر إحداث نقلة نوعية في قطاع الاتصالات العالمية.
وقد أدت هذه التطورات في مجال الاتصالات الألياف البصرية في انخفاض الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية لعدة أنواع من الاتصالات. على سبيل المثال، يتم إجراء نقل بين المواقع الثابتة أو الاتصالات من نقطة إلى نقطة، حيث يطلب من عرض النطاق الترددي كبيرة (مثل شبكات الهاتف عبر المحيطات) من خلال الألياف البصرية بدلا من استخدام الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية. يستخدم الألياف البصرية الاتصالات أيضا لنقل الإشارات الهاتفية، الاتصال عبر شبكة الإنترنت، والشبكة المحلية (LAN جيجابت) وإشارات التلفزيون كابل.
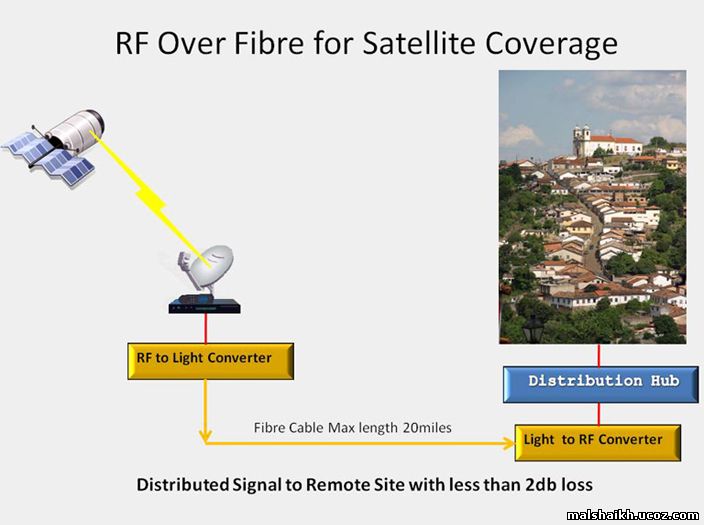
الاتصالات الفضائية
استخدام الاتصالات الفضائية الأقمار الصناعية كما التبديلات بين المرسل والمتلقي في مواقع مختلفة على الأرض. أنظمة الأقمار الصناعية تسمح للمستخدمين لتجاوز مكاتب الناقل نموذجية وتبث المعلومات إلى مواقع متعددة. وتستخدم الأقمار الصناعية للاتصالات للإذاعة والتلفزيون والهاتف والانترنت والعسكرية وغيرها من التطبيقات. هناك أكثر من 2000 الأقمار الصناعية حول مدار الأرض، وتستخدم للاتصال من قبل كل من الحكومة والمنظمات الخاصة.
الاتصالات للأقمار الصناعية هي لوس (خط البصر) أنظمة الميكروويف مع مكرر. هذه الأقمار تدور حول الأرض مع سرعة الأرض، والمعروفة باسم الأقمار الصناعية الثابتة بالنسبة للأرض. القيود المفروضة على حجم الهوائي أيضا حدود التركيز القدرة على جعل تغطية الارسال قمر صناعي واحد كبير جدا. وهذا يجعل الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية مثالية لخدمات التلفزيون والراديو وإشارة يجب أن تنبع من نقطة واحدة إلى العديد من النقاط في اتجاه واحد. المسافة كبيرة من الأقمار الصناعية من الأرض (حوالي 22،300 ميل) نتائج في تأخير الأمر الذي يؤثر سلبا الآثار في اتجاهين الاتصالات مثل المحادثات النقالة. الأقمار الصناعية المدار الأرضي المنخفض يمكن أن تستخدم في الاتصالات المتنقلة في اتجاهين لأنه مطلوب طاقة أقل للوصول إلى تلك الأقمار الصناعية.
المقارنة بين الألياف البصرية والاتصالات الفضائية
- عرض النطاق الترددي وبيانات الأسعار: الألياف البصرية يدعم ارتفاع أسعار عرض النطاق الترددي والبيانات بالمقارنة مع الأقمار الصناعية.
- التنقل: الألياف البصرية لا يمكن استخدامها في تطبيقات الهاتف المحمول وغير مناسبة لمواقع ثابتة. الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية هو مناسبة لتطبيقات الهاتف المحمول.
- الموثوقية: الألياف البصرية الاتصالات هو أكثر موثوقية من الأقمار الصناعية.
- التضاريس: الألياف الضوئية هو أكثر ملاءمة للمناطق الحضرية والسهول حيث حفر / زرع أسهل. الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية مناسب للمناطق النائية والمناطق الوعرة مثل المناطق الجبلية.
- تأخير: الألياف البصرية لديه الحد الأدنى أو أي صنع التأخير غير مناسبة للتطبيقات في الوقت الحقيقي. الاتصالات عبر الأقمار الصناعية لديه تأخير نشر الأصيل.
- التدخل: الألياف البصرية لديها أقل أو أي التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي EMI بينما الاتصالات الساتلية يحتوي على نسبة عالية EMI.
- تغطية: الأقمار الصناعية هي مناسبة لتوفير نقطة إلى خدمات متعددة نقطة مع تغطية واسعة مثل التلفزيون والراديو.
- كلفة:
- التكلفة الأولية: يعتمد على حجم الشبكة وما إذا كان المستخدم يريد أن نشر شبكة كاملة أو جزء منها وتأجير بقية.
- التكلفة المتكررة: الأقمار الصناعية لديها التكلفة المتكررة أعلى من الاتصالات من الألياف البصرية.
English version:
Optic fiber communication and satellite communication are the leading technologies which are revolutionizing the world of telecommunications. Both technologies have their advantages and limitations which make them suitable for certain type of applications. This article will provide an overview of optic fiber and satellite communication technologies and present a comparison of the features and related issues.
Optic Fiber Communication
Optic Fiber communication transmits information by sending pulses of light (using laser) through an optic fiber. The low signal loss in optic fibers and high data rate of transmission systems, allow signals with high data rates (exceeding several Gbps) to travel over long distances (more than 100 km) without a need of repeater or amplifier. Moreover, using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) allows a single fiber to carry multiple signals (up to 10 different signals) of multi-Gbps transmissions. Optic Fiber communication offers extremely high bandwidth, immunity to electromagnetic interference, non-existent delays and immunity from interception by external means. In the 1980s and 1990s, the continents were linked together using undersea optic fiber bringing about a paradigm shift in the global telecommunications.
These advancements in optic fiber communication has resulted in decrease of satellite communications for several types of communications. For instance, transmission between fixed locations or point-to-point communications, where large bandwidths are required (such as transoceanic telephone systems) are made through optic fiber instead of using satellite communication. Optic Fiber communication is also used to transmit telephone signals, Internet communication, LAN (Gigabit LAN) and cable television signals.
Satellite Communication
Satellite communications use artificial satellites as relays between a transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Satellite systems allow users to bypass typical carrier offices and to broadcast information to multiple locations. Communications satellites are used for radio, TV, telephone, Internet, military and other applications. There are more than 2,000 satellites around Earth’s orbit, being used for communication by both government and private organizations.
Communication Satellites are LOS (line-of-sight) microwave systems with a repeater. These satellites rotate around the earth with the speed of earth and are known as geostationary satellites. The limitations of antenna size also limits focusing capability making the coverage for a single satellite transmitter very large. This makes satellite communication ideal for TV and radio services as the signal has to flow from a single point to many points in a single direction. The large distance of satellites from the earth (about 22,300 miles) results in delays which adversely effects two-way communication like mobile conversations. Low earth orbit satellites can be used for two-way mobile communication because less power is required to reach those satellites.
Comparison of Optic Fiber and Satellite Communication
- Bandwidth and data rates: Optic Fiber supports higher bandwidth and data rates as compared to satellite.
- Mobility: Optic Fiber cannot be used in mobile applications and is suitable for fixed locations. Satellite communication is suitable for mobile applications.
- Reliability: Fiber Optic communication is more reliable than satellite.
- Terrain: Fiber optic is more suitable for urban areas and plains where digging / laying is easier. Satellite communication is suitable for remote areas and rough terrains like mountainous areas.
- Delay: Optic fiber has minimum or no delays making is suitable for real time applications. Satellite communication has an inherent propagation delay.
- Interference: Optic fiber has less or no Electromagnetic Interference EMI whereas Satellite communication has high EMI.
- Coverage: Satellites are suitable for providing point to multi-point services with large coverage like TV and radio.
- Cost:
- Initial Cost: Depends on the size of network and whether the user wants to deploy complete network or part of it and lease the rest.
- Recurring Cost: Satellite has higher recurring cost than optic fiber communication.
|
Serial
|
Feature
|
Optic Fiber
|
Satellite
|
|
1
|
Bandwidth
|
Higher
|
Lower
|
|
2
|
Data rates
|
Higher
|
Lower
|
|
3
|
Mobility
|
Not mobile
|
Mobile
|
|
4
|
Reliability
|
Higher
|
Lower
|
|
5
|
Terrain
|
Urban areas, plains
|
Mountainous terrain and remote areas
|
|
6
|
Delay
|
No delay
|
Delay in transmission
|
|
7
|
Interference
|
No EMI
|
High EMI
|
|
8
|
Cost
|
Lower recurring cost
|
Higher recurring cost
|
|