ترددات الراديو (RF) الاتصالات اللاسلكية هو الشكل الرئيسي للاتصالات اللاسلكية كما يتم استخدامه في التلفزيون والإذاعة وأنظمة الهاتف الخلوي والشبكات اللاسلكية والعديد من التطبيقات الأخرى.

وكان ظهور الاتصالات اللاسلكية شهدت صعود الأنظمة التناظرية التي معظمها تم استبدالها الآن الأنظمة الرقمية بسبب المزايا التي تتيحها التكنولوجيات الرقمية. هذه المادة سوف يقدم لمحة عامة عن التكنولوجيا اللاسلكية RF، التناظرية والاتصالات اللاسلكية الرقمية وسوف ترسم مقارنة بين التقنيات اللاسلكية اثنين.
RF (الترددات الراديوية) التكنولوجيا اللاسلكية
نظم الاتصالات اللاسلكية RF لها الارسال والاستقبال. منذ حجم الهوائي يجب أن يكون كبير مثل ربع الطول الموجي، والإشارة الأصلية (عادة صوت) لا يمكن أن تنتقل دون نقلها على التردد العالي (الطول الموجي أقل) الذي يقلل من حجم الهوائي. من ناحية النقل، وفرضه على الإشارة الأصلية (عادة صوت) على إشارة RF المولدة محليا يسمى الناقل – عملية توصف بأنها التشكيل. إشارة الحامل التي تحتوي على المعلومات، ثم يتم تنتقل عن طريق الهوائي. وتلقى بعد ذلك في المستقبل حيث يتم استخراج المعلومات من الناقل التضمين – عملية تسمى الإستخلاص. خلال انتشار الإشارة في الفضاء الحر للإشارة يصبح أضعف ويحصل مشوهة بسبب تأثيرات الضجيج ونشر مثل التفكير، والحيود ونثر. آثار تشويه أسوأ في الأنظمة المتنقلة حيث البيئة تتغير من لحظة إلى أخرى. التقنيات اللاسلكية التناظرية والرقمية وفي الواقع تستخدم لتمكين نقل واستقبال مع الحد من مشاكل تشويه خلال نشر.
التناظرية التكنولوجيا اللاسلكية
في الأنظمة التناظرية، وتستخدم إشارات متفاوتة تردد أو السعة لتعديل الموجات الحاملة. الإشارات التناظرية تتغير باستمرار (قيم لانهائية) وتمثل على شكل سلسلة من موجات جيبية. وAM و FM البث الإذاعي هي الأمثلة الأكثر شيوعا لانتقال التناظرية.
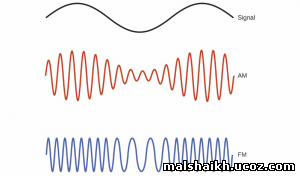
في AM (السعة التحوير) اتساع الإشارة الأصلية (صوت) يستخدم لتعديل الناقل والإشارة المرسلة لديه معلومات في اتساع الموجة الحاملة.
في حين، في FM (تردد التحوير) تردد الإشارة الأصلية (صوت) يستخدم لتعديل الناقل والإشارة المرسلة لديه معلومات في وتيرة تغيير الموجة الحاملة.
واستندت الجيل الأول (1G) المعايير الخلوية المتنقلة مثل الامبير (أي إم بي إس) وNMT (الشمال موبايل تليفون) على تكنولوجيات الاتصال التناظرية. وقد أدخلت هذه في 1980s، وحلت محلها معايير 2G التي تعتمد على تقنيات الخلوية الرقمية بحلول نهاية 1990s أو 2000s في وقت مبكر.

التكنولوجيا اللاسلكية الرقمية
في الأنظمة الرقمية، إشارات منفصلة (مجموعة محدودة أو محدودة من القيم) في الوقت وقيمة ويتم تمثيلها الأرقام الثنائية، “0” أو “1” (كل طالب قليلا).

الإشارات الرقمية يمكن توليدها عن طريق أخذ عينات من مستمرة (التناظرية) إشارة حيث تحاول الإشارة الرقمية لتقريب قيم الإشارات التناظرية في خطوات منفصلة صغيرة.
تقنيات التشكيل من الإشارة اللاسلكية الرقمية هي أكثر تعقيدا من تلك الإشارات التناظرية. منذ مطلوب الطيف الترددي لتتم مشاركتها بين المستخدمين في المنطقة، وتوفر تقنيات الترددات اللاسلكية الرقمية عدد من التقنيات وصول متعددة.
· في FDMA (تردد الانقسام وصول متعددة)، وينقسم الطيف في فتحات تردد حيث يتم تعيين كل فتحة لمستخدم واحد في وقت واحد.
· في TDMA (الوصول المتعدد بالتقسيم الزمني)، وينقسم الطيف الترددي في فتحات الوقت حيث يتم تعيين كل فتحة لمستخدم واحد في وقت واحد.
· • وفي سى دى ام ايه (سي دي إم أيه) لكافة المستخدمين استخدام نفس التردد الحامل وقد نقل في وقت واحد. كل مستخدم لديه كلمة السر الخاصة المزيف والتي يتم استخدامها في المستقبل لتحديد المرسل. سى دى ام ايه هي تقنية الرقمية التي تسمح 8-15 مرات أكثر للمستخدمين استيعابها في نفس النطاق الترددي بالمقارنة مع التقنيات التناظرية.
أحدث التقنيات الخلوية GSM، 3G و 4G LTE كلها أمثلة على التقنيات الرقمية. التقنيات الرقمية توفر العديد من المزايا أكثر من النظم التناظرية وخاصة عدد كبير من المستخدمين يمكن استيعابها في عرض النطاق الترددي المتوفر.
المقارنة – بث مقابل الراديو الرقمي تردد التقنيات اللاسلكية
- الضوضاء: الإشارات التناظرية هي أقل تحملا للضجيج في حين الإشارات الرقمية هي أكثر تسامحا بكثير للضوضاء.
- سلامة البيانات: استخدام التقنيات التناظرية، أخطاء أثناء الإرسال يمكن أن تفسد الرسالة. في خطأ وتستخدم تقنيات تصحيح لتجديد رسالة وتوفير الحصانة ضد الضوضاء.
- تتطلب النظير إشارات أقل عرض النطاق الترددي في حين تتطلب الإشارات الرقمية المزيد من عرض النطاق الترددي: عرض النطاق الترددي. ومع ذلك، يمكن للتقنيات الرقمية استيعاب عدد أكبر من المستخدمين في نفس النطاق الترددي مقارنة الإشارات التناظرية.
- المستخدمين / الوصول المتعدد: في التقنيات التناظرية، وأقل المستخدمين يمكن استيعابها في عرض نطاق معين في حين أن استخدام التقنيات الرقمية المزيد من المستخدمين يمكن استيعابها في عرض نطاق معين بسبب تقنيات وصول متعددة أكثر كفاءة.
- مضاعفة: عن قنوات يمكن المضاعفة في عرض نطاق معين في التكنولوجيات الرقمية بالمقارنة مع التناظرية.
- مرونة الأجهزة: في الأنظمة التناظرية والأجهزة ليست مرنة. ومن محددة ومطلوبة للتغيير مع تغير في التردد. ومع ذلك، في الأنظمة الرقمية والأجهزة مرنة حيث إشارات RF يمكن التعامل معها من قبل بسيطة، أجهزة الاستقبال والإرسال موحدة، والإشارة الرقمية يمكن بعد ذلك التعامل مع في القاعدي أو البرامج.
- حجم الأجهزة: جهاز الإرسال والاستقبال في الأنظمة التناظرية هي كبيرة في حجم حين الأنظمة الرقمية صغيرة من ذلك بكثير في الحجم.
- الخدمات: يتم استخدام أنظمة التناظرية لخدمات الصوت والفيديو. وتستخدم الأنظمة الرقمية للصوت والفيديو والبيانات.
- لا يمكن تخزينها الإشارات التناظرية على الكمبيوتر حين الإشارات الرقمية يمكن معالجتها بسهولة وتخزينها على جهاز الكمبيوتر: تخزين.
- إشارة خلط: الإشارات التناظرية لا يمكن أن تكون مختلطة بسهولة في حين إشارات رقمية متعددة يمكن أن تكون مختلطة بسهولة.
- حزمة الشبكات / الإنترنت: لا يمكن packetized الإشارات التناظرية (إلا إذا رقمية). في حين أن الإشارات الرقمية يمكن packetized لإرسال عبر شبكات الحزمة مثل الإنترنت.
- ضغط: محدود ضغط ممكن في الإشارات التناظرية في حين أن أعلى ضغط يمكن أن يتحقق في الإشارات الرقمية•
English version
Radio Frequency (RF) wireless communication is the leading form of wireless communication as it is being used in TV, radio, cellular phone systems, wireless networking and several other applications. The advent of RF communications had seen the rise of analog systems which have now mostly been replaced by digital systems due to the advantages offered by the digital technologies. This article will present an overview of RF wireless technology, analog and digital wireless communication and will draw a comparison between the two RF technologies.
RF Wireless Technology
RF wireless communication systems have a transmitter and a receiver. Since the size of antenna has to be as large as one-fourth of the wavelength, the original signal (normally voice) cannot be transmitted without transferring it onto a higher frequency (smaller wavelength) that reduces size of the antenna. On the transmission side, the original signal (normally voice) is superimposed on a locally generated RF signal called a carrier – a process termed as modulation. The carrier signal containing the information, is then transmitted by the antenna; and then received at receiver where the information is extracted from the modulated carrier – a process called demodulation. During propagation of the signal in free space the signal becomes weaker and gets distorted due to noise and propagation effects like reflection, diffraction and scattering. Distortion effects are worse in mobile systems where the environment is changing from one moment to the other. The analog and digital RF technologies are in fact used to enable the transmission and reception while reducing the problems of distortion during propagation.
Analog Wireless Technology
In analog systems, signals of varying frequency or amplitude are used to modulate the carrier waves. Analog signals are continuously changing (infinite values) and are represented as a series of sine waves. The AM and FM radio transmissions are the most common examples of analog transmission.

Figure 1 – Original Signal, AM and FM Modulated Signals
In AM (Amplitude Modulation) the amplitude of the original signal (voice) is used to modulate the carrier and the transmitted signal has the information in the amplitude of the carrier wave. Whereas, in FM (Frequency Modulation) the frequency of the original signal (voice) is used to modulate the carrier and the transmitted signal has the information in the changing frequency of the carrier wave.
The first generation (1G) mobile cellular standards like AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) and NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone) were based on analog communication technologies. These were introduced in 1980s and were replaced by 2G standards which were based on digital cellular technologies by end 1990s or early 2000s.

Figure 2 – AMPS Phone
Digital Wireless Technology
In digital systems, signals are discrete (finite or limited set of values) in time and value and are represented by binary numbers, “0” or “1” (each called a bit).

Figure 3 – Original Signal, Analog and Digital Signal
The digital signals can be generated by sampling of continuous (analog) signal where the digital signal tries to approximate the values of analog signal in small discrete steps.

Figure 4 – Analog to digital conversion
The modulation techniques of digital wireless signal are more complicated than those of analog signals. Since the frequency spectrum is required to be shared among users in an area, digital RF technologies provide a number of multiple access techniques.
- In FDMA (frequency division multiple access), spectrum is divided into frequency slots where each slot is assigned to a single user at any one time.
- In TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access), frequency spectrum is divided into time slots where each slot is assigned to a single user at any one time.
- In CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) all users use the same carrier frequency and may transmit simultaneously. Each user has its own pseudorandom code word which is used at the receiver to identify the sender. CDMA is a digital technique which allows 8-15 times more users to be accommodated in the same bandwidth as compared to analog technologies.
The latest cellular technologies GSM, 3G and 4G LTE all are examples of digital technologies. Digital technologies offer several advantages over analog systems especially a large number of users can be accommodated in the available bandwidth.
Comparison – Analog vs Digital RF Wireless Technologies
- Noise: Analog signals are less tolerant to noise whereas digital signals are much more tolerant to noise.
- Data Integrity: Using analog technologies, errors during transmission can corrupt the message. In Error correction techniques are used to regenerate message and provide immunity against noise.
- Bandwidth: Analog signals require less bandwidth whereas digital signals require more bandwidth. However, digital technologies can accommodate more users in the same bandwidth as compared to analog signals.
- Users / Multiple Access: In analog techniques, less users can be accommodated in a given bandwidth whereas using digital techniques more users can be accommodated in a given bandwidth due to more efficient multiple access techniques.
- Multiplexing: More channels can be multiplexed in a given bandwidth in digital technologies as compared to analog.
- Flexibility of hardware: In analog systems, hardware is not flexible. It is specific and required to be changed with change in frequency. However, in digital systems the hardware is flexible where RF Signals can be handled by simple, standardized receivers and transmitters, and the digital signal can be then dealt with in baseband or software.
- Size of Hardware: The transmitter and receiver in analog systems are large in size whereas digital systems are much small in size.
- Services: Analog systems are used for voice and video services. Digital systems are used for voice, video and data.
- Storage: Analog signals cannot be stored on computer whereas digital signals can be easily processed and stored on computer.
- Signal mixing: Analog signals cannot be easily mixed whereas multiple digital signals can be easily mixed.
- Packet networks / Internet: Analog signals cannot be packetized (unless digitized). Whereas digital signals can be packetized to send over packet networks like Internet.
- Compression: Limited compression is possible in analog signals whereas higher compression can be achieved in digital signals.
|
Serial
|
Factor
|
Analog
|
Digital
|
|
1
|
Data
|
Continuous
|
Discrete (finite)
|
|
2
|
Representation
|
Uses continuous range of values to represent information
|
Uses discrete or discontinuous values to represent information
|
|
3
|
Signalling
|
Continuously varying electromagnetic wave
|
Sequence of voltage pulses
|
|
4
|
Waves
|
Denoted by sine waves
|
Denoted by square waves
|
|
5
|
Noise
|
Less tolerant to noise
|
More tolerant to noise
|
|
6
|
Data Integrity
|
Errors during transmission can corrupt the message
|
Error correction techniques are used to regenerate message and provide immunity against noise
|
|
7
|
Bandwidth
|
Low bandwidth
|
High bandwidth
|
|
8
|
Users / Multiple Access
|
Less users can be accommodated in a given bandwidth
|
More users can be accommodated in a given bandwidth due to better multiple access techniques
|
|
9
|
Multiplexing
|
Less channels can be multiplexed
|
More channels can be multiplexed
|
|
10
|
Flexibility of hardware
|
Hardware is not flexible. It is specific and required to be changed with change in frequency
|
Flexible. RF Signals can be handled by simple, standardized receivers and transmitters, and the digital signal can be then dealt with in baseband or software.
|
|
11
|
Hardware size -Transmitter and receiver
|
Large in size
|
Small in size
|
|
12
|
Services
|
Voice and video
|
Voice, video and data
|
|
13
|
Storage
|
Not easily stored on computer
|
Easily stored on computer
|
|
14
|
Signal mixing
|
Cannot be mixed
|
Can be easily mixed
|
|
15
|
Packet networks / Internet
|
Cannot be packetized
|
Can be packetized to send over packet networks like Internet
|
|
16
|
Compression
|
Limited compression possible
|
Higher compression can be achieved
|
|